
Business Payment Card: Business Credit Cards
- Finance
- Corporate Cards
- 28-Feb-24
What is a Business Payment Card?
It is often referred to as a corporate card or commercial card, is a financial tool specifically designed to streamline and facilitate business-related transactions. These cards are distinct from personal credit card or debit card & are tailored to meet the unique needs of your business in India.

Types of Business Payment Cards
Business Credit Cards:
Description: Business credit cards are a common and versatile option for companies. A corporate credit card provides a revolving line of business credit that allows businesses to make purchases up to a predetermined limit. The outstanding balance can be paid off in full each month or carried over with interest for a business credit card.
Benefits:
Flexibility in managing cash flow; interest free credit is also available
Potential reward points, including cash back, travel reward points, fuel surcharge waiver or to get a bunch of other perks.
Access to credit for business expenses via business credit card; separate from a personal card to use
Debit Cards:
Description: Business debit cards are linked to a company's bank account and enable direct access to available funds. When used, the purchase amount is deducted directly from the business's checking account.
Benefits:
No interest charges, as transactions are funded from available account balances.
Real-time tracking of expenses, helping with budget management.
Often issued with spending controls for added security.
Prepaid Cards:
Description: Prepaid business cards are loaded with a specific amount of funds in advance. Businesses can only spend the preloaded amount & once depleted, the card needs to be reloaded.
Benefits:
Control over spending, as the cardholder cannot exceed the prepaid amount.
No risk of accumulating debt, as spending is limited to the preloaded funds.
Useful for budgeting & controlling expenses.

Virtual Cards:
Description: Virtual business cards exist purely in digital form and are typically used for online transactions. They do not have a physical counterpart & often come with dynamic card numbers for added security.
Benefits:
Enhanced security with dynamic card numbers that change with each transaction.
Convenient for online & digital transactions.
Easy issuance & distribution, especially for remote or digital teams.\

What is a Credit Card?
A credit card is a payment card issued by a financial institution, typically a bank, that allows the cardholder to borrow funds to make purchases. Unlike a debit card, which deducts funds directly from the user's bank account, a credit card provides a revolving line of credit up to a predetermined limit. This means that the cardholder can spend up to the credit limit & the outstanding balance can be paid off either in full by the due date or carried over with interest on the remaining balance. Essentially, a credit card serves as a short-term loan, providing individuals with the flexibility to spend money they may not have immediately.

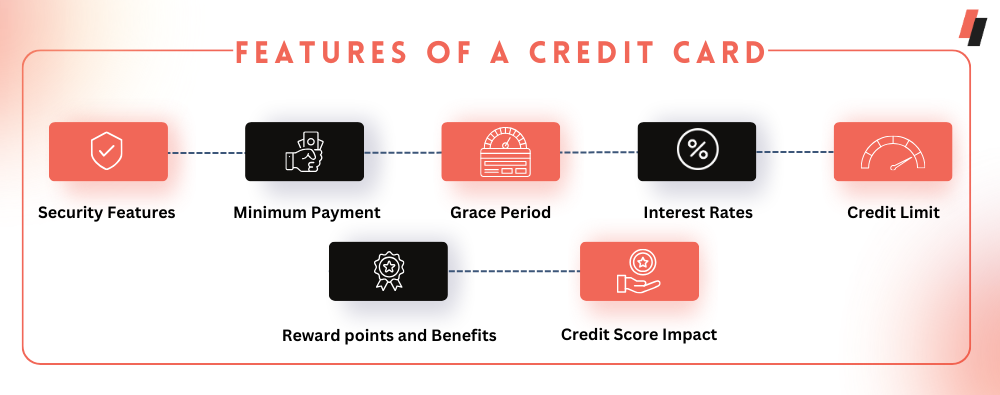
Here are key features and components of a credit card:
Credit Limit:
The credit limit is the maximum amount a cardholder can borrow on a credit card. It is determined by the card issuer based on factors such as the cardholder's credit history, income, and overall creditworthiness.
Interest Rates:
Credit cards typically have an Annual Percentage Rate (APR), which represents the cost of borrowing on the card. If the cardholder carries a balance beyond the grace period (the time between the end of a billing cycle & the due date), interest is charged on the remaining balance.
Grace Period:
The grace period is the time during which the cardholder can pay the outstanding balance in full without incurring interest charges. This period usually lasts from the end of a billing cycle to the due date.
Minimum Payment:
The minimum payment is the smallest amount a cardholder must pay by the due date to keep the account in good standing. It typically includes interest charges & a percentage of the outstanding balance.
Reward points and Benefits:
Many credit cards and business cards offer reward points, including cash back, travel reward points, or points that can be redeemed for various perks. Some cards also come with additional benefits such as travel insurance, purchase protection, & extended warranties.
Security Features:
Credit cards often include security features like EMV chips, which provide added protection against fraud. Cardholders are also protected by regulations that limit their liability for unauthorized transactions.
Credit Score Impact:
The use of a credit card and the repayment history can impact the cardholder's credit score. Responsible use, including timely payments & maintaining a low credit utilization ratio, can positively affect credit scores.
How Credit Cards Work:
Card Application: To obtain a credit card, individuals must apply with a financial institution or credit card issuer. The application process involves providing personal information, income details, and consent for a credit check for the credit card.
Approval and Credit Limit: Upon approval, the cardholder receives the credit card along with a credit limit. This limit is the maximum amount the cardholder can spend using the credit card.
Making Purchases: Cardholders can use their credit cards to make purchases at various merchants, both online and offline. The credit card issuer pays the merchant on behalf of the cardholder.
Monthly Statements: Credit card issuers provide monthly statements detailing the transactions made, the outstanding balance & the minimum payment due. Cardholders can choose to pay the full balance or make a minimum payment.
Repayment: Responsible credit card use involves timely repayment. In case of Failing to pay the full balance by the due date may result in interest charges & negatively impact the cardholder's credit score.

Credit cards offer convenience and flexibility for making purchases, both in-person and online. A credit card is widely accepted globally, making them a popular choice for consumers.
What is a Business Credit Card?
A business credit card is a card for specifically designed for business-related transactions. Similar to personal use credit cards, business credit cards provide a line of credit that allows for a small business to make purchases, cover expenses, manage cash flow and reward points on spends. A business credit card is issued to businesses or business owners and are intended for use in funding various operational needs for a small business.

Challenges with a Business Credit Card
High-Interest Rates:
Business credit cards often come with higher interest rates compared to other financing options. If businesses carry a balance from month to month, interest charges can accumulate, potentially leading to increased debt.
Fees and Charges:
Business credit cards may impose various fees, such as annual fees, late payment fees, cash advance fees, and foreign transaction fees. These fees can add up, impacting the overall cost of using the card.
Debt Accumulation:
The ease of access to credit can lead to debt accumulation, especially if businesses do not manage their spending and repayment responsibly. Accumulating debt can strain the company's financial health and affect its creditworthiness.
Credit Score Impact:
Late payments or consistently carrying high balances on a business credit card can negatively impact the business owner's personal credit score. This, in turn, may affect the business's ability to secure favorable financing terms in the future.
Limited Credit Access for New Businesses:
Startups and new businesses may find it challenging to qualify for business credit cards, as issuers often require a business credit history. In the absence of an established credit history, business owners may need to rely on personal credit or explore alternative financing options instead of a business credit card.
Potential for Employee Misuse:
Issuing a business credit card to employees for business expenses introduces the risk of misuse. Without proper controls and monitoring, employees may make unauthorized purchases or exceed spending limits, leading to financial challenges for the business.
Security Concerns:
Business credit cards, like any financial tool, are susceptible to fraud and security breaches. Unauthorized transactions, identity theft, or card information compromise can pose significant challenges and require swift resolution.
Complex Expense Tracking:
While business credit cards offer features for expense tracking, the process can become complex, especially for businesses with numerous transactions. Sorting and categorizing expenses may require additional time and resources.

Introducing Prepaid Cards
A prepaid card is a payment card that is preloaded with a specific amount of funds, allowing the cardholder to make purchases up to the prepaid balance for small business. Unlike credit cards that provide a line of credit or debit cards linked to a bank account, prepaid cards are not connected to a traditional banking account. Instead, users load funds onto the card in advance, and transactions are processed as long as the available balance covers the purchase amount.

Types of Prepaid Cards:
General-Purpose Prepaid Cards:
These cards are widely accepted and can be used for various purchases, both in-store and online.
Gift Cards:
Prepaid gift cards are often designed for a specific retailer or brand and are a popular choice for gift-giving, users can also earn cashback on their spends.
Travel Cards:
Prepaid travel cards are convenient for individuals traveling abroad, allowing them to load foreign currencies and avoid currency exchange fees.
Payroll Cards:
Employers may use prepaid cards to disburse salaries and employee benefits. This method is especially beneficial for unbanked or underbanked employees.

Benefits of Prepaid Cards:
Controlled Spending:
Users can only spend the available balance, promoting responsible and controlled spending.
No Credit Checks:
Prepaid cards do not require a credit check, making them accessible to individuals with varying credit histories.
Financial Inclusion:
Prepaid cards can be instrumental in providing financial services to unbanked or underbanked individuals who may not have access to traditional banking.
Security and Fraud Protection:
With features like PIN protection and limited exposure to personal information, prepaid cards offer enhanced security against fraud.
Budgeting Tools:
Many prepaid card providers offer online platforms or mobile apps with budgeting tools, helping users track their expenses and manage finances more effectively.

Best Practices for Managing Business Expenses Efficiently
Create a Comprehensive Budget:
Develop a detailed budget that outlines income, fixed costs, variable expenses, and discretionary spending. Regularly review and update the budget to reflect changing business conditions.
Prioritize Spending:
Identify and prioritize essential expenses that are crucial for business operations. Ensure that these critical expenses are funded before allocating resources to discretionary items.
Implement Spending Policies:
Establish clear spending policies and guidelines for employees. Clearly communicate spending limits, approval processes, and the types of expenses that are permissible. This helps prevent unnecessary or unauthorized expenditures.
Use Technology for Expense Tracking:
Leverage accounting software and expense management tools to track and categorize expenses. Automation can streamline the process, reduce errors, and provide real-time visibility into spending patterns.

Centralize Purchasing:
Centralize purchasing responsibilities to consolidate buying power and negotiate better deals with suppliers. This can help eliminate duplicate purchases and ensure consistency in procurement.
Monitor Cash Flow:
Keep a close eye on cash flow to ensure that the business has enough liquidity to cover operational expenses. Implement effective invoicing and payment collection processes to maintain a healthy cash position.
Leverage Business Payment Cards:
Use business credit cards or prepaid cards to streamline transactions, monitor spending, and take advantage of reward points. Implement controls, such as spending limits and transaction monitoring, to manage card usage effectively.
Review and Cut Unnecessary Expenses:
Regularly review all expenses to identify areas where costs can be cut without compromising productivity or quality. Eliminate non-essential subscriptions, services, or discretionary spending that does not contribute to the company's goals.
Employee Training on Spending Policies:
Ensure that employees are well-informed about spending policies and procedures. Provide training on expense reporting, reimbursement processes, and the importance of adhering to budgetary constraints.
Forecast Future Expenses:
Develop forecasts for future expenses based on historical data and business projections. Anticipate upcoming costs and allocate resources accordingly to avoid last-minute financial strain.
